The most advanced MPE+ sound engine
The EaganMatrix is a MPE+ modular digital synth engine invented by Edmund Eagan, utilizing a purpose-designed DSP engine by Lippold Haken.
The EaganMatrix allows the user to finely craft their musical sound by digitally connecting audio and control modules via a patching matrix. Every patch point in the Matrix can be programmed to have anywhere from zero human input, to being completely under the control of a human finger.
The EaganMatrix synthesizer is internal to the Continuum Fingerboard, the ContinuuMini, and Expressive E’s Osmose keyboard. The EaganMatrix comes with the Haken Editor, a dedicated desktop editor for preset creation.
A limitless expressive patchbay
The EaganMatrix is based on this fundamental observation: HOW you control a sound algorithm is at least as important as the QUALITY of the sound algorithm.
In the EaganMatrix, data is continuously analyzed, optimized, and transferred at a sub-millisecond rate to intimately control synthesis parameters. The design of the EaganMatrix allows for an “organic" connection between the player and the instrument that is reminiscent of a player’s interaction with an acoustic instrument.
Our engine was inspired by classical modular matrix patching synthesizers such as the ARP 2500 and the EMS Synthi 100. However, unlike those analog predecessors, the EaganMatrix has moved far beyond using pins to make patch point connections.
A Complete Continuum Walkthrough
Instead, equations can be placed inside a selected patch point, replacing that static pin, creating a simple to amazingly complex relationship between the Continuum/Osmose playing surface and the flow of sound from patch point source to destination. Each 3D performance direction of the Continuum playing surface can influence the final result of every single patch point. And there are many, many patch points!
In the EaganMatrix, patch sources are on the left of the matrix, and patch destinations are above the matrix. To make a connection, a value or formula is inserted in the intersection point of the source and the destination.
A detailed User Guide for the EaganMatrix can be downloaded in the support section of this web site.
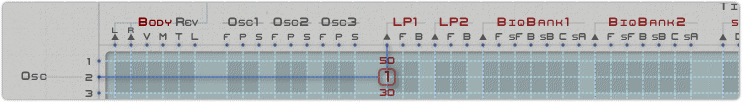
Patching example
Above, a section of the matrix showing a highlighted connection:
Direct + using Formula C into Oscillator 3 frequency
Connection points can use a wide variety of constants, predefined formulas, or user-defined formulas. Usage of user-defined formulas can be monitored in the Formula thumbnail area of the EaganMatrix, pictured to the left on this page.
In the picture below, the highlighted patch point shows a constant of 1 patched from Oscillator 2 source to LowPass filter 1 input, allowing the audio from the Oscillator to go directly into the filter without influence from the playing surface.
A section of the matrix, showing a highlighted connection:
Osc 2 using Constant 1 into Low Pass filter 1 input
The connection highlighted below shows a predefined Formula, Z, being used to control the audio output of Filter 1 into the right input of the Master section. Formula Z is a predefined mapping of the Continuum surface, only using the pressure (Z) value from finger placement. Used this way the finger acts as a volume control for the filter level.
A section of the matrix, showing a highlighted connection:
Filter 1 using Predefined formula Z into Audio Right Out
Sound modules
There are a number of source and destination modules available, everything from oscillators and filters to direct formulas. Here is a partial listing of currently available modules:
1. 5 flexible summation oscillators, each with controls for frequency, phase, and spectral balance. The oscillators can also act as waveshapers, creating rich harmonic variations to the oscillator input.
2. A smooth organic-sounding noise source, as well as up to five seeded noise sources.
3. 5 versatile multimode filters, with these inputs: audio to be filtered, frequency, and bandwidth. Possible two-pole filters are LowPass, HighPass, BandPass, LowShelf and HighShelf, as well as unity gain BandPass, Notch, and AllPass; single-pole low pass and high pass filters are also available. Filters can be cascaded for cutoff of 12, 24, 36, or 48 dB/octave (6, 12, 18, and 24 dB/octave for single pole filters)
4. 2 powerful biquad filter banks, which are banks of 8 or 48 related but independent biquad filters, with controls for audio input, frequency, frequency spread, bandwidth, bandwidth spread, spectral centre, and spectral weighting. These biquads are the core technology for Modal Physical Models commonly used with the Continuum Fingerboard. These banks can also act as granular synthesis modules, as vocal mouth shapes, or additive synthesis modules.
5. Time delays, with controls for audio input and time. Time delays are suitable for creating chorus and flanging effects, and can be used for echo delays as well. These time delays are the core technology for Waveguide Physical Models and Feadback Delay Network (FDN) effects.
6. Five independent Shape Generators (SGs), each with controls for cycle mode, frequency, and trigger. Available generator shapes are RampUp, RampDown, Pulse, Triangle, Hann, Square, Sine, and SampleAndHold. The SGs have been integrated into the EaganMatrix a unique way, allowing each SG to influence a formula result directly.
7. 8 CVC (Continuum Voltage Convertor) outputs, allowing matrix preprocessing of control voltages. This requires that a CVC be connected to the Continuum.
8. Master Section with convolution and recirculator (reverb and reverb-like processing) controls common to all voices.
A detailed EaganMatrix User Guide can be downloaded in the support section of this web site.